Controls [vb.net] VB.NET으로 이벤트 로그 생성 및 읽기, 쓰기 및 삭제
페이지 정보

본문
이벤트 로그 기록을 위해 우선 MSDN 자료를 찿아 보았습니다.
CreateEventSource(String, String)
오버로드
CreateEventSource(EventSourceCreationData) | 이벤트 소스와 해당 이벤트 로그에 대한 지정된 구성 속성을 사용하여 지역화된 이벤트 메시지를 작성할 올바른 이벤트 소스를 설정합니다. |
CreateEventSource(String, String) | 로컬 컴퓨터의 로그에 엔트리를 쓰는 유효한 이벤트 소스로 지정된 소스 이름을 설정합니다. 또한 이 방법을 사용하면 로컬 컴퓨터에 새로운 사용자 지정 로그를 만들 수도 있습니다. |
CreateEventSource(String, String, String) | 사용되지 않습니다. 지정된 컴퓨터의 로그에 엔트리를 쓰는 유효한 이벤트 소스로 지정된 소스 이름을 설정합니다. 또한 이 방법을 사용하면 지정한 컴퓨터에 새로운 사용자 지정 로그를 만들 수도 있습니다. |
친절하게도 설명이 되어 있습니다. ㅠ.ㅠ;;
"CreateEventSource(String, String)" 이런 식으로 되어 있고
그 옆 설명을 보아도....
관련해서 다른 도움말을 찾아 보았습니다.
public static void CreateEventSource (string source, string logName);
이제 좀 이해가 되지만 어떤 식으로 기록이 되는지 궁금해집니다.
그래서 구글링을 하던 중 이해가 한 번에 되는 자료를 찾게 되었습니다.
Imports System.Diagnostics '// 출처
Dim aLog As EventLog Dim myLog As New EventLog Dim aEventLogList() As EventLog Dim aLogEntry As EventLogEntry Dim aLogEntries As EventLogEntryCollection ' ' Create a new log. ' If Not EventLog.SourceExists("MyNewSource") Then EventLog.CreateEventSource("MyNewSource", "MyNewLog") End If ' ' Add an event to fire when an entry is written. ' AddHandler myLog.EntryWritten, AddressOf OnEntryWritten
With myLog .Source = "MyNewSource" .Log = "MyNewLog" .EnableRaisingEvents = True ' ' Write a few entries. ' .WriteEntry("Writing Error entry to event log", EventLogEntryType.Error) .WriteEntry("Writing Information entry to event", EventLogEntryType.Information) .WriteEntry("Writing Warning entry to event", EventLogEntryType.Warning) ' ' Output all events in the new log. ' aLogEntries = .Entries() For Each aLogEntry In aLogEntries With aLogEntry Console.WriteLine( _ "Source: {0}" & vbCrLf & _ "Category: {1}" & vbCrLf & _ "Message: {2}" & vbCrLf & _ "EntryType: {3}" & vbCrLf & _ "EventID: {4}" & vbCrLf & _ "UserName: {5}", _ .Source, .Category, .Message, .EntryType, .EventID, .UserName) End With Next ' ' Delete your new log. ' .Clear() .Delete("MyNewLog") ' ' Output the names of all logs on the system. ' aEventLogList = .GetEventLogs() For Each aLog In aEventLogList Console.WriteLine("Log name: " & aLog.LogDisplayName) Next End With
Public Sub OnEntryWritten(ByVal source As Object, ByVal e As EntryWrittenEventArgs) Console.WriteLine(("Written: " + e.Entry.Message)) End Sub |
위 프로그램 소스를 이해하고 아래와 같이 만들어 테스트해봤습니다.
Imports System.Security.Principal |
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click If Not IsAdministrator() Then MsgBox("관리자 권한으로 실행해 주시기 바랍니다.") If Not EventLog.SourceExists("program1472") Then _ EventLog.CreateEventSource("program1472", "IT_HUB") Dim myLog As EventLog = New EventLog() myLog.Source = "program1472" myLog.WriteEntry("Writing to event log.") End Sub
Public Function IsAdministrator() As Boolean Dim identity As WindowsIdentity = WindowsIdentity.GetCurrent() If identity IsNot Nothing Then Dim principal As New WindowsPrincipal(identity) Return principal.IsInRole(WindowsBuiltInRole.Administrator) End If Return False End Function |
"CreateEventSource(String, String)"을 좀더 이해하기 위해
※ 여기서 중요한 건 관리자 권한으로 실행을 해야 EventLog를 사용할 수 있습니다.
'윈도 로고+R' 단축키를 눌러 실행 창에 'eventvwr.msc' 명령어를 입력 후 '확인' 버튼을 누릅니다.
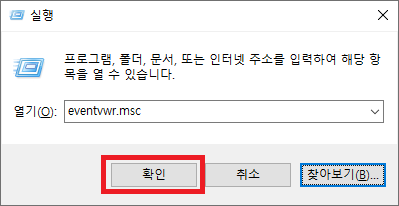
"응용 프로그램 및 서비스 로그"에 많이 보던 단어가 보이네요..
"IT_HUB"를 클릭해봤습니다.
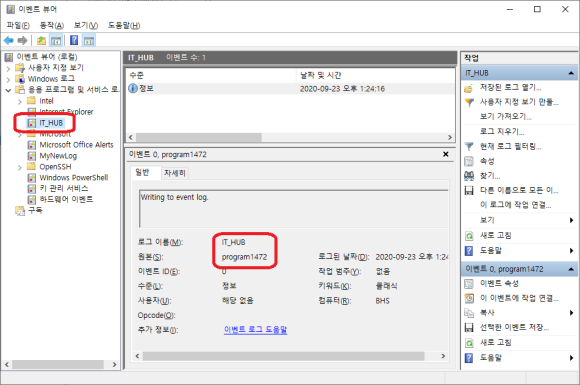
헉.... 이 사진 한 장이면 ..... 모든 설명이 되겠죠?
※ 결론은 사용안하는 걸로.....
- 이전글DataTable에서 중복되지 않는 유일한 값 추출 및 ComboBox에 아이템 추가하는 예제 20.10.06
- 다음글[vb.net] DateTimePicker 표시형식 변경 20.09.15
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.